How to Use Dynamic DNS with ACTi Cameras There are surveillance solutions that consist of single cameras scattered over a wide territory, therefore each of those cameras should be connected to Internet in order to become accessible by Control Center. For example, the chain stores, bus stops, currency exchange booths, etc.
In such cases, one of the practical networking solutions is to use DSL modem on camera site and let the camera obtain the dynamic IP address from the Internet Service Provider through the DSL modem using PPPoE connection, which is much more cost-effective than applying for static IP address.
However, there is one drawback in this solution – in order to do the remote surveillance from the Control Center, the NVR Server in the Control Center has to know the address of the IP camera at all times in order to get the video stream from the camera. If the camera’s network connection has been reset for any reason, the camera will get a new IP address through DSL Modem, which may be different from the previous one. NVR will not know about this change, and the connection between the camera and NVR will fail.
The good news is – there exists a solution that makes sure the NVR can find the camera even if the camera IP changes frequently. ACTi cameras support Dynamic DNS service that allows frequently changing IP be mapped to a certain unchangeable domain name. The mapping database and its updating engine are hosted in one of the Dynamic DNS servers, most of which offer basic services for free, such as www.dyndns.org.
Every time the IP camera gets an IP that is different from previous one, it notifies the public DDNS Service about the change. The DDNS Service updates its database immediately, mapping the assigned domain name (for example tcm7411.dyndns.org) to the new IP address.
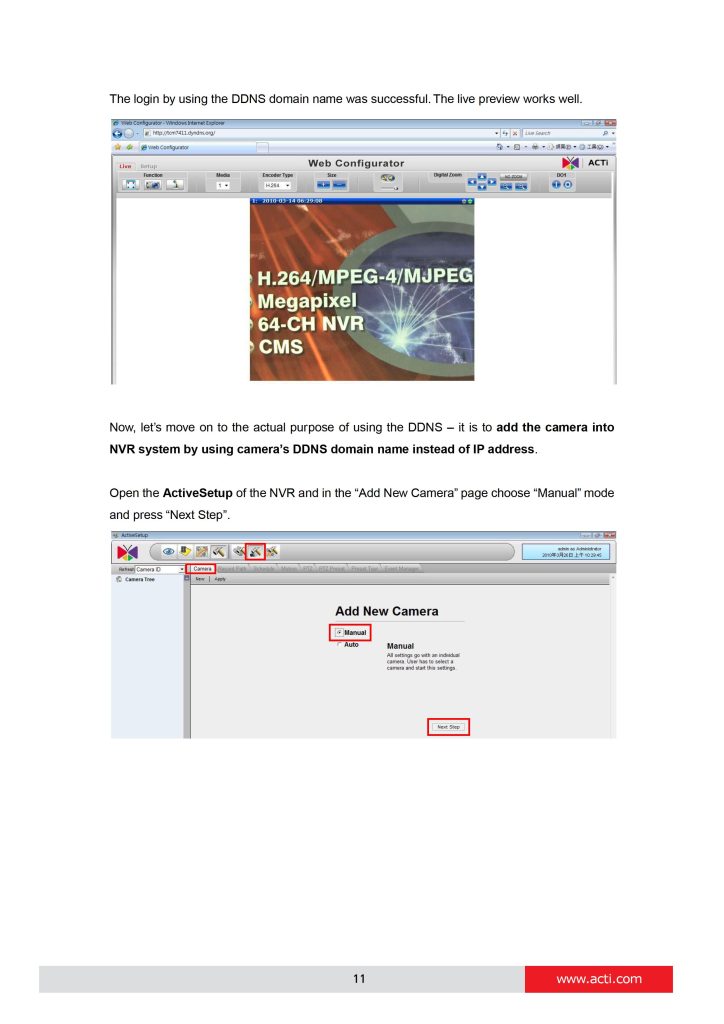
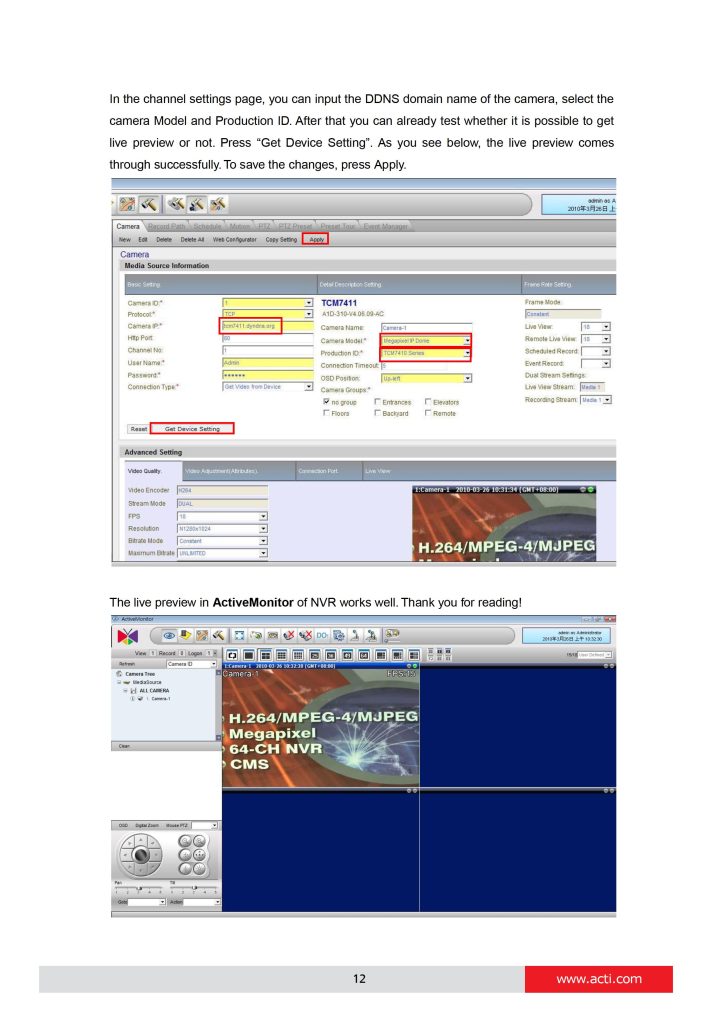
In NVR settings, only the domain name (tcm7411.dyndns.org) is used to identify the camera.
Every time when NVR needs to connect to the camera, it asks from DDNS Service what the current camera’s IP is. The DDNS Service instantly responds to NVR and tells it the camera’s IP. Now NVR will use the IP of the camera to connect to the camera and the video stream from the camera to NVR can be initiated.
As a result, NVR can always find the IP camera regardless of frequently changing IP address of the camera. Since there are so many public DDNS Services available for free, the PPPoE-based connection is really a good and low-cost solution for single-camera sites.
Although the theoretical explanation might be clear by now, you might still want to know the step-by-step procedure of how to set up the PPPoE together with DDNS support.



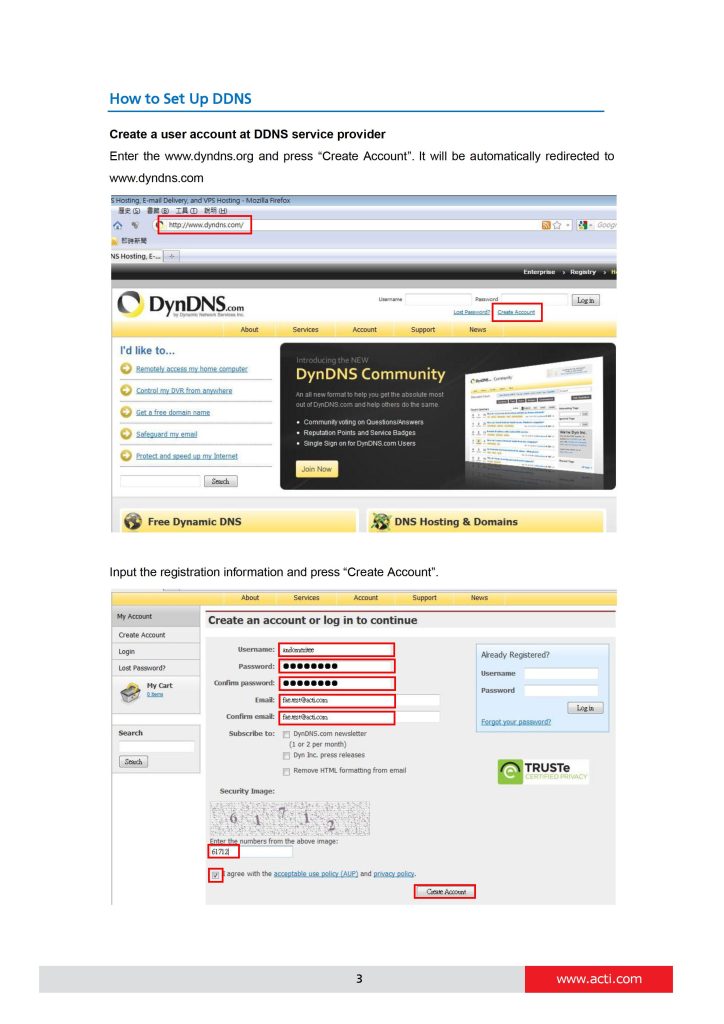
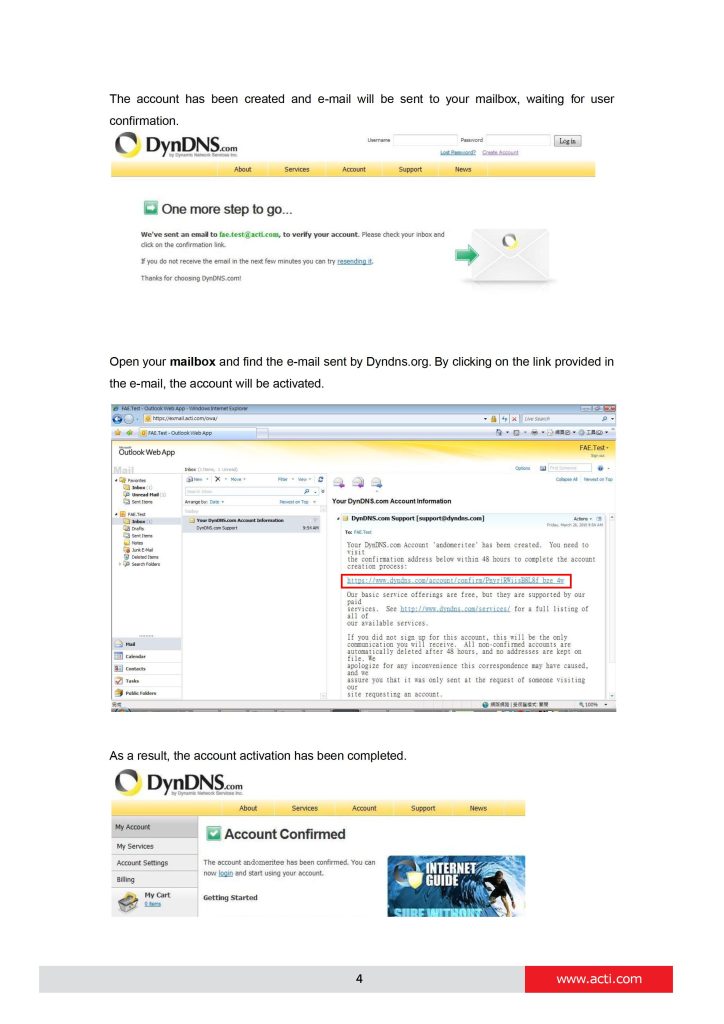

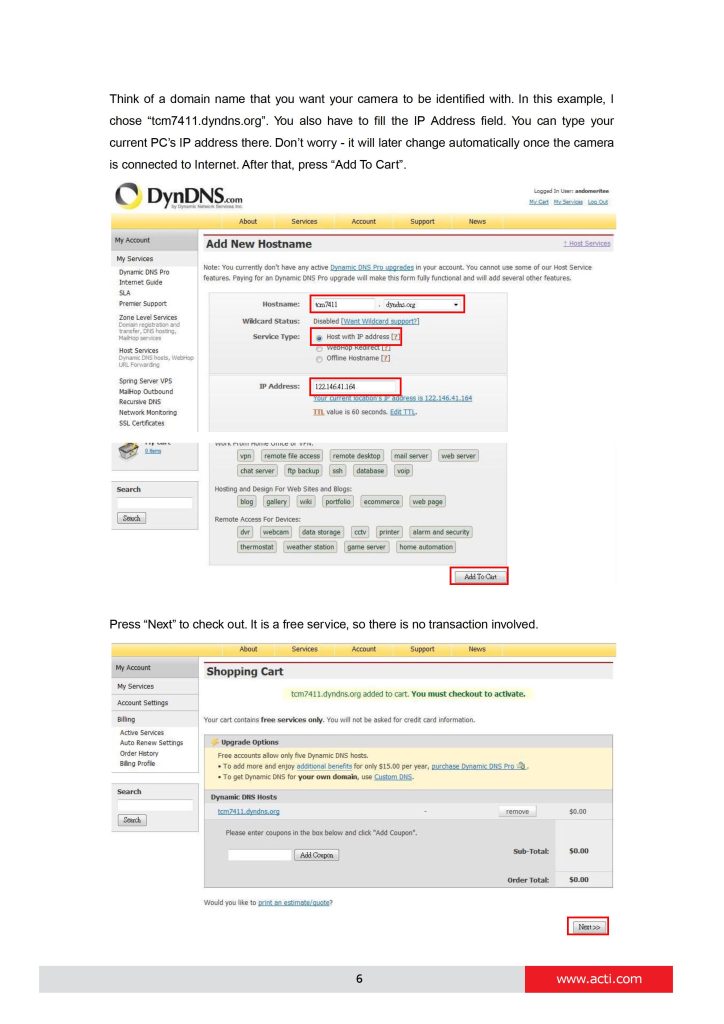
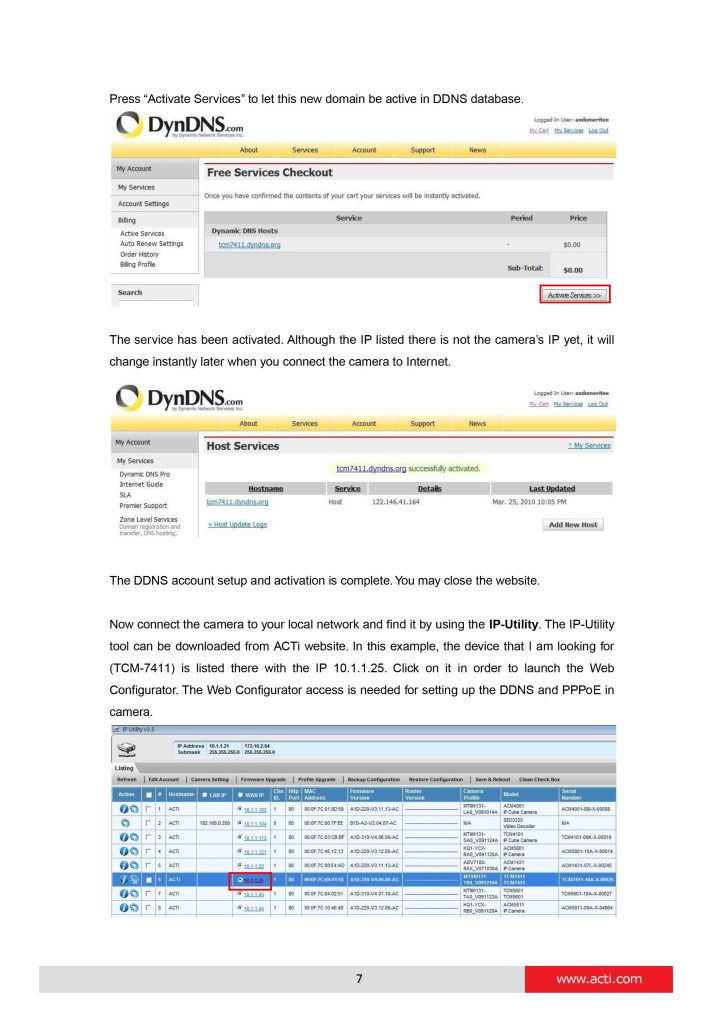
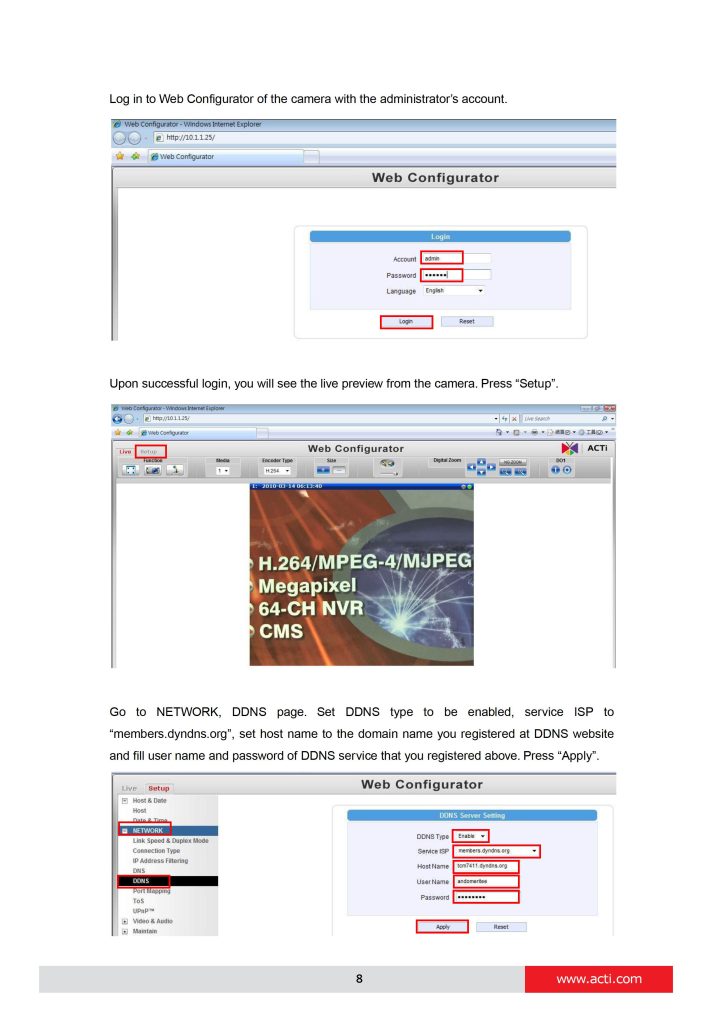
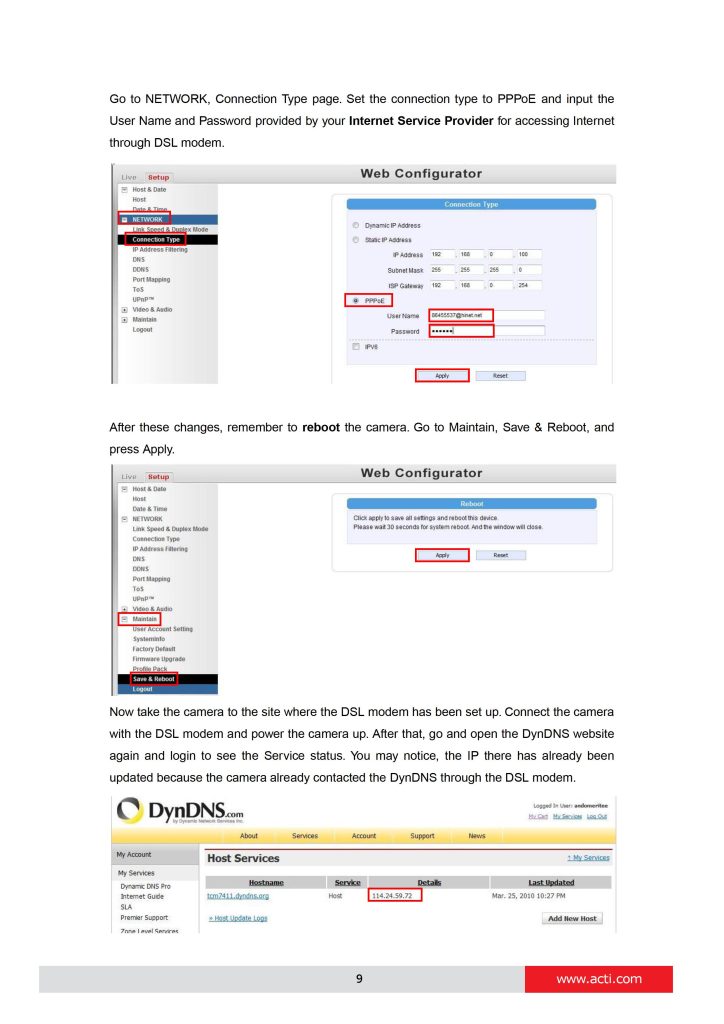
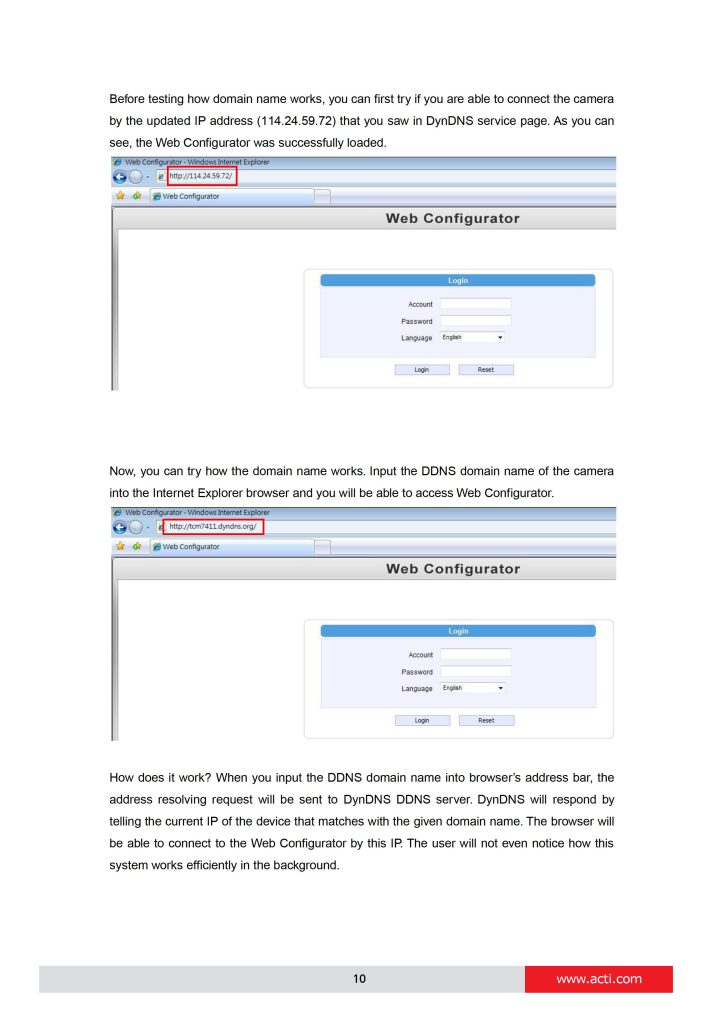




can you help me please
I sent an e-mail from the communication channel. Can you help?